1975 Omaha tornado outbreak
41°15′N 96°00′W / 41.25°N 96°W
| Type | Tornado outbreak |
|---|---|
| Duration | May 6–7, 1975 |
| Tornadoes confirmed | 36 |
| Max. rating1 | F4 tornado |
| Duration of tornado outbreak2 | ~2½ days |
| Fatalities | 3 fatalities, 137+ injuries |
| Damage | $250-300 million [1975 USD] |
| Areas affected | Midwestern and Southern United States |
| 1Most severe tornado damage; see Fujita scale 2Time from first tornado to last tornado | |
The 1975 Omaha tornado was a violent tornado that hit the Omaha metropolitan area in the U.S. state of Nebraska. It was the costliest and most powerful tornado out of 36 that touched down across the Midwest and South during the two-day outbreak. Besides Nebraska, South Dakota, Iowa, Texas Mississippi, and Louisiana were all affected by multiple tornadoes which resulted in millions of dollars [USD] in damages.
Meteorological synopsis[edit]
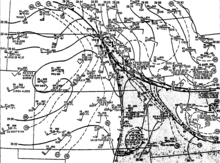
The tornado outbreak was associated with an intense area of low pressure that moved from Colorado into South Dakota beneath a strong upper-tropospheric trough. The combination of the low-pressure system and a ridge of high pressure over the Great Lakes moved unstable air in the lower levels of the troposphere towards eastern Nebraska.[1] At 7 a.m. CDT on May 6,[a] the area of low pressure was centered over southwestern South Dakota, with a central air pressure of 991 mbar (hPa; 29.26 inHg). A cold front extended from the low-pressure system southwestward to central Kansas, demarcating the boundary between a moist and warmer airmass to the east and a dry and cooler airmass to the west. Ahead of the cold front over eastern Kansas and Nebraska, dew points were near 65 °F (18 °C) while they were below 20 °F (−7 °C) behind the cold front over western Kansas.[2] An ongoing scientific field campaign run by NASA – Atmospheric Variability Experiments – sampled environmental conditions throughout the southwestern and southern United States during the eventual severe weather event.[3][4] A weather balloon launched from Omaha, Nebraska, at 7 a.m. sampled atmospheric conditions moderately conducive to severe weather.[5] During the morning hours, the broader wind pattern brought increasingly moist air in the lower troposphere into a narrow region encompassing eastern Nebraska, eastern Kansas, and northern Missouri.[6] This corridor of moist air was bounded to the west by the cold front and to the east by a warm front, each slowly moving.[7] Warmer and drier air persisted in the mid-levels of the troposphere above this moist air, resulting in conditions potentially favorable for the development of storms.[8] Daytime heating and the increase in moisture with time within this narrow region, as well as a simultaneous divergence of air in the upper-troposphere, further increased atmospheric instability, producing increasingly favorable conditions for storm formation.[9] Ahead of the warm front, thunderstorms and cloud cover over southern Iowa and northern and central Missouri caused cooler conditions ahead of the warm front, reinforcing a strong temperature gradient across the front.[10] This further enhanced the favorability of atmospheric conditions for storm development.[11]
The National Severe Storms Forecast Center (NSSFC) issued a tornado watch for much of the area in advance of the event at 12:37 p.m. May 6.[1][12] The watch area was in effect from 2–8 p.m. and encompassed parts of eastern Nebraska, northeastern Kansas, northwestern Missouri, western Iowa, southeastern South Dakota, and southwestern Minnesota;[12][13] Omaha was also included within the watch area.[14] The first indications of storm development were apparent in South Dakota by 11 a.m.[15] A squall line soon developed along much of the cold front, with the strongest thunderstorms occurring near the intersection between the cold and warm fronts ahead of the low-pressure area and along the warm front, including the storm that eventually produced a destructive tornado in Omaha.[8][10] Within this area, vorticity and convergence of winds near the surface were higher than surrounding areas.[16] The squall line was first apparent on weather radar at around 1 p.m., extending from central South Dakota to central Oklahoma.[17] At around 1:15 p.m., the National Weather Service office in Omaha received a report of hail from Creigton, the office's first of the day.[18] Between around 2–7 p.m., the squall line produced several damaging tornadoes in northeastern Nebraska.[17] In the Omaha area, the development of thunderstorms was preceded by the movement of a comma-shaped area of cloudiness into the region, an indication of the movement of vorticity in the mid- to upper-troposphere into the region.[5] Many of the thunderstorms that produced tornadoes showed rapid growth on satellite imagery around the time of tornado development, indicative of the rapid rise of air.[19] The thunderstorms were supported by the channel of moist air, tracking north before eventually weakening after moving into cooler and drier air downwind.[10] Twelve tornadoes ultimately occurred over the north-central Great Plains on May 6,[1] with large and strong tornadoes affecting eastern Nebraska.[20] All but one of the tornadoes had relatively short tracks, with their parent thunderstorms moving across the narrow corridor of moist air and the steep temperature gradient accompanying the warm front; the storm that produced the long-track tornado moved parallel to the temperature gradient.[21] The same weather system led to at least 19 tornadoes on May 7, including 10 in South Dakota and Iowa.[1]
Confirmed tornadoes[edit]
| FU | F0 | F1 | F2 | F3 | F4 | F5 | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 8 | 8 | 17 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 37 |
- Note: One tornado is confirmed, but its rating is unknown
| Color / symbol | Description |
|---|---|
| † | Data from Thomas Grazulis |
| ※ | Data from the 1975 Storm Data publication |
| ‡ | Data from the NCEI database |
May 6 event[edit]
| F# | Location | County / Parish | State | Start Coord. | Time (UTC) | Path length | Max width |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F2 | Near Ola to S of Chamberlain | Brule | SD | 43°38′N 99°05′W / 43.63°N 99.08°W | 17:00–?※ | 12 mi (19 km) | 50 yd (46 m) |
| Numerous farm buildings were destroyed across four farms, and five cattle were killed. The NCEI lists this tornado at F0 intensity, but it is assessed at F2 strength by Grazulis.[22][23] | |||||||
| F4 | E of Pierce to N of Magnet | Pierce, Cedar | NE | 42°12′N 97°34′W / 42.20°N 97.57°W | 19:05–? | 19 mi (31 km) | 300 yd (270 m) |
| A violent tornado moved through Magnet on a southeasterly to northwesterly heading at around 2:15 p.m. CDT, damaging or destroying nearly every structure in town.[22][23][24][25] The Magnet city hall was destroyed.[24] Some homes were completely leveled. Cattle were killed, cars were thrown over 200 yd (180 m), and power lines were toppled. One person was injured.[22][23] Meteorologist Ted Fujita, who later photographed cycloidal scar patterns left by the tornado in cornfields in Cedar and Pierce counties,[26][27] estimated that the tornado that struck Magnet was stronger the Omaha tornado.[1] | |||||||
| F2 | SW of Pierce, NE to SW of Yankton, SD | Pierce, Knox, Cedar | NE | 42°10′N 97°28′W / 42.17°N 97.47°W | 19:15–?† | 43 mi (69 km)† | 90 yd (82 m) |
| A strong tornado caused damage intermittently along its path, especially in western Pierce where homes were damaged, barns were destroyed, cars were tossed, power lines were toppled, and livestock were killed. The NCEI lists this tornado at F3 intensity, but it is assessed at F2 strength by Grazulis.[22][23] | |||||||
| F0 | W of Bloomfield | Knox | NE | 42°31′N 97°46′W / 42.52°N 97.77°W | 19:30–? | 5.4 mi (8.7 km)‡ | 30 yd (27 m) |
| Farm buildings, irrigation equipment, and trees were sporadically damaged.[22] | |||||||
| F3 | SE of Stanton to NE of Carroll | Stanton, Wayne | NE | 41°58′N 97°12′W / 41.97°N 97.20°W | 19:45–?† | 25 mi (40 km)† | 150 yd (140 m) |
| An intense tornado caused extensive damage to farms and power lines. Multiple barns were leveled, and one home was reduced to two standing walls. Five hundred chickens were killed. One person was injured.[22][23] | |||||||
| F2 | SE of Tyndall to NW of Scotland† | Bon Homme, Hutchinson† | SD | 42°56′N 97°45′W / 42.93°N 97.75°W | 19:46–? | 20 mi (32 km)† | 80 yd (73 m)† |
| Small farm buildings were damaged. The Storm Data publication and the NCEI consider this event as two separate tornadoes focused in Bon Homme County. However, they are considered one event by Grazulis, and the path was extended into Hutchinson County. Additionally, the NCEI lists this tornado at F1 intensity, but it is assessed at F2 strength by Grazulis.[22][23] | |||||||
| F0 | W of Scotland | Bon Homme | SD | 43°09′N 98°04′W / 43.15°N 98.07°W | 20:10–? | 5.4 mi (8.7 km) | 33 yd (30 m) |
| Small farm buildings were damaged.[22] | |||||||
| F0 | E of Colon | Saunders | NE | 41°17′N 96°35′W / 41.28°N 96.58°W | 21:00–? | 3.4 mi (5.5 km) | 17 yd (16 m) |
| A brief tornado caused damage to trees and farm buildings on two farms.[22] | |||||||
| F0 | SW of Waterbury | Dixon | NE | 42°26′N 96°45′W / 42.43°N 96.75°W | 21:30–? | 3 mi (4.8 km) | 80 yd (73 m) |
| Trees, power lines, and farm buildings were damaged.[22] | |||||||
| F4 | Omaha | Sarpy, Douglas | NE | 41°10′N 96°04′W / 41.17°N 96.07°W | 21:33–21:50※ | 10 mi (16 km) | 250 yd (230 m) |
| 3 deaths – See the section on this tornado | |||||||
| F2 | NE of Crescent to E of Beebeetown | Pottawattamie, Harrison | IA | 41°24′N 95°51′W / 41.40°N 95.85°W | 22:00–22:30※ | 11 mi (18 km) | 500 yd (460 m) |
| Numerous farm houses and outbuildings were damaged or destroyed.[22] An aluminum silo was lofted 0.75 mi (1.21 km) away from a farmstead southwest of Beebeetown, Iowa.[28] This tornado is not listed in Thomas Grazulis' Significant Tornadoes book.[23] | |||||||
| F2 | N of Honey Creek to S of Logan | Pottawattamie, Harrison | IA | 41°28′N 95°52′W / 41.47°N 95.87°W | 22:20–22:45※ | 13 mi (21 km) | — |
| Numerous farm houses and outbuildings were damaged or destroyed over intermittent stretches of a tornado's path.[22] This tornado is not listed in Thomas Grazulis' Significant Tornadoes book.[23] | |||||||
May 7 event[edit]
| F# | Location | County / Parish | State | Start Coord. | Time (UTC) | Path length | Max width |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F2 | S of Pioneer | West Carroll | LA | 32°40′N 91°28′W / 32.67°N 91.47°W | 06:05–? | 5.6 mi (9.0 km) | — |
| A manufactured home was destroyed, and the occupant was severely injured after being tossed across the road. Portions of the home were scattered for 3 mi (4.8 km). Another house lost its roof and had its furniture tossed. The occupants were trapped and injured by a fallen tree.[22][23] | |||||||
| F1 | N of Natchez | Adams | MS | 31°37′N 91°24′W / 31.62°N 91.40°W | 11:45–? | 0.25 mi (0.40 km) | 60 yd (55 m) |
| A farm co-op building had one of its sides knocked down and its roof ripped off and subsequently wrapped around a utility pole. A concession stand was destroyed, a warehouse was damaged, and several tree tops were twisted.[22] | |||||||
| F1 | E of Midland | Jones | SD | 44°04′N 100°54′W / 44.07°N 100.90°W | 16:55–? | — | — |
| A brief tornado caused some property damage.[22] | |||||||
| F1 | Hattiesburg | Forrest | MS | 31°19′N 89°19′W / 31.32°N 89.32°W | 17:10–? | 0.25 mi (0.40 km) | 18 yd (16 m) |
| Several pavilion shelters in Kemper Park were blown down. Playground equipment was damaged, power lines were toppled, and trees were uprooted. Some tree limbs fell onto a car.[22] | |||||||
| F1 | S of Richton | Perry | MS | 31°19′N 89°00′W / 31.32°N 89.00°W | 17:50–? | 9.7 mi (15.6 km) | 440 yd (400 m) |
| Trees were uprooted, some of which fell on a manufactured home and a car, injuring the occupant.[22] | |||||||
| F1 | E of Wendte | Stanley | SD | 44°15′N 100°36′W / 44.25°N 100.60°W | 18:00–? | — | — |
| A brief tornado caused some property damage.[22] | |||||||
| F2 | WSW of Eastabuchie to Providence | Forrest, Jones | MS | 31°24′N 89°23′W / 31.40°N 89.38°W | 19:30–? | 5.4 mi (8.7 km) | 150 yd (140 m) |
| Two houses lost their roofs while a third was heavily damaged. Two chicken houses were destroyed and trees were uprooted, some of which fell on homes or blocked roads.[22][23] | |||||||
| F0 | N of Pierre | Sully | SD | 44°42′N 100°24′W / 44.70°N 100.40°W | 19:55–? | — | — |
| A brief tornado was reported to the sheriff's office.[22] | |||||||
| F0 | NE of Pierre | Sully | SD | 44°38′N 100°08′W / 44.63°N 100.13°W | 21:30–? | — | — |
| A brief tornado was reported to the sheriff's office.[22] | |||||||
| F1 | Leander | Williamson | TX | 30°35′N 97°51′W / 30.58°N 97.85°W | 22:00–? | — | — |
| An F1 tornado caused damage in Leander.[29] | |||||||
| F2 | Nolanville | Bell | TX | 31°05′N 97°37′W / 31.08°N 97.62°W | 22:00–23:00 | — | — |
| Four manufactured homes were demolished, one was overturned, and eleven others were damaged. Two people were injured.[22] This tornado is not listed in Thomas Grazulis' Significant Tornadoes book.[23] | |||||||
| F0 | NW of Pierre | Sully | SD | 44°45′N 100°48′W / 44.75°N 100.80°W | 22:20–? | — | — |
| A brief tornado was reported to the sheriff's office.[22] | |||||||
| F? | Burnet | Burnet | TX | — | 22:30–? | — | — |
| Small buildings and sheds were blown down, and trees were uprooted. This tornado is listed in the Storm Data publication but not by the NCEI.[29] | |||||||
| F2 | S of Dow City | Crawford | IA | 41°49′N 95°30′W / 41.82°N 95.50°W | 23:30–? | — | — |
| Grain bins, a brick silo, and a machine shed were destroyed. The roof was ripped off a feeding shed. A garage was overturned. A home lost shingles and windows.[22] This tornado is not listed in Thomas Grazulis' Significant Tornadoes book.[23] | |||||||
| F2 | E of Harlan to Irwin | Shelby | IA | 41°39′N 95°13′W / 41.65°N 95.22°W | 00:00–? | 12 mi (19 km)※ | — |
| Some farm buildings, a barn, and a corn crib were destroyed. The roof of a home was damaged.[22] This tornado is not listed in Thomas Grazulis' Significant Tornadoes book.[23] | |||||||
| F0 | Creston | Union | IA | 41°04′N 94°22′W / 41.07°N 94.37°W | 00:15–? | — | — |
| A tornado touched down in an open field.[22] | |||||||
| F2 | E of Grand River | Decatur | IA | 40°49′N 93°50′W / 40.82°N 93.83°W | 01:00–?※ | — | — |
| Two hog houses and a barn were destroyed. Two hogs were killed. Trees were uprooted as well.[22][23] | |||||||
| F2 | Osceola | Clarke | IA | 41°02′N 93°47′W / 41.03°N 93.78°W | 01:30–?※ | 10 mi (16 km) | — |
| A strong tornado caused damage at six farms. A barn and a shed were destroyed. The roof and doors were ripped off a house, windows were blown out of a car, and two cows were killed.[22][23] | |||||||
May 8 event[edit]
| F# | Location | County / Parish | State | Start Coord. | Time (UTC) | Path length | Max width |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F2 | S of Florien | Sabine | LA | 31°20′N 93°40′W / 31.33°N 93.67°W | 04:00–? | — | — |
| A tornado destroyed a home and then moved through forested areas.[22] This tornado is not listed in Thomas Grazulis' Significant Tornadoes book.[23] | |||||||
| F2 | Northeastern Welsh | Jefferson Davis | LA | 30°14′N 92°49′W / 30.23°N 92.82°W | 06:05–? | 1 mi (1.6 km) | 100 yd (91 m) |
| Six homes and four trailers were destroyed, including one trailer lofted to the tops of trees. Numerous trees were uprooted. Three people were injured.[22][23] | |||||||
| F1 | Mansfield | DeSoto | LA | 32°02′N 93°43′W / 32.03°N 93.72°W | 06:15–? | 0.75 mi (1.21 km) | — |
| A brief tornado uprooted trees, one of which fell onto a home, injuring the occupant.[22] | |||||||
| F2 | S of Estherwood | Acadia | LA | 30°10′N 92°29′W / 30.17°N 92.48°W | 07:00–? | 0.25 mi (0.40 km) | 50 yd (46 m) |
| A manufactured home was destroyed. A number of aircraft at a hangar were damaged at the Le Gros Airport.[22] This tornado is not listed in Thomas Grazulis' Significant Tornadoes book.[23] | |||||||
| F1 | Duson | Lafayette | LA | 30°14′N 92°11′W / 30.23°N 92.18°W | 07:30–? | 0.5 mi (0.80 km) | 50 yd (46 m) |
| An auto repair shop and several manufactured homes were damaged. Two people were injured.[22] | |||||||
| F2 | Baton Rouge | East Baton Rouge | LA | 30°25′N 91°11′W / 30.42°N 91.18°W | 07:30–? | 6.2 mi (10.0 km) | 50 yd (46 m) |
| A tornado impacted the Louisiana State University campus, ripping the tops of elevator shafts and the top half of a nearby water tower. Numerous trees were snapped or twisted.[22] This tornado is not listed in Thomas Grazulis' Significant Tornadoes book.[23] | |||||||
| F2 | SW of Greensburg | St. Helena | LA | 30°45′N 90°45′W / 30.75°N 90.75°W | 08:00–? | — | — |
| Six electrical transmission towers were destroyed.[22] This tornado is not listed in Thomas Grazulis' Significant Tornadoes book.[23] | |||||||
Omaha, Nebraska[edit]
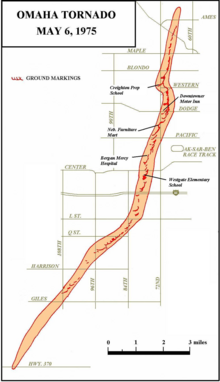 Path of the Omaha tornado | |
| Meteorological history | |
|---|---|
| Formed | May 15, 1975 c. 4:33 p.m. CDT (UTC−05:00) |
| Dissipated | c. May 15, 1975 c. 4:50 p.m. CDT (UTC−05:00) |
| Duration | ~17 minutes |
| F4 tornado | |
| on the Fujita scale | |
| Overall effects | |
| Fatalities | 3 |
| Injuries | 141 |
| Damage | $150–200 million (1975 USD) $0.8–1.1 billion (2023 USD) |
| Houses destroyed | 287 |
| [12] | |
During the early afternoon of Tuesday, May 6, 1975, a tornado watch was issued for much of eastern Nebraska. Initial tornado activity started in northeast Nebraska throughout the first half of the afternoon. At around 4:15 PM, a tornado warning was issued for the Omaha area and an F4 tornado[30] touched down about 15 minutes later in Sarpy County, Nebraska. The storm then moved north-east, cutting into Douglas County crossing Interstate 80 (injuring several motorists) and through west-central sections of the city of Omaha. The tornado chopped a path across 10 miles (16 km) of streets and residences, crossing the city's busiest intersection at 72nd & Dodge. Extensive damage occurred along 72nd Street, with numerous homes and apartments severely damaged, along with Creighton Prep School and the United Methodist Church. The Westgate subdivision was devastated, with many homes leveled, and a few that were swept away. The nearby Westgate Elementary School was destroyed. Bergan Mercy Hospital, Lewis and Clark Junior High School, a motel, and several industrial buildings were severely damaged as well. The tornado later lifted in the Benson Park area at 4:58.[31]
In one remarkable instance, First United Methodist Church minister of music Mel Olson spotted the rolling clouds in the sky outside the windows of the room where he was rehearsing a children's choir. He led them to safety below the church building. The building, located at 70th and Cass Streets, was struck and heavily damaged by the twister. The room where the children had been practicing, with three walls of windows, was hit and the glass exploded.
Three people were killed and 133 others were injured. One of the fatalities was a woman who was thrown by the tornado from her home to a backyard four or five houses away.[32] At least 287 buildings were destroyed, and nearly 4,000 buildings were damaged with debris found, in some cases, several miles away. When adjusted for inflation, this remains one of the costliest tornadoes in United States history.
See also[edit]
- List of North American tornadoes and tornado outbreaks
- Tornado outbreak of April 26–28, 2024 – produced several significant tornadoes in the Omaha area
- Tornado outbreak sequence of March 1913 – included a damaging and deadly tornado in Omaha
Notes[edit]
- ^ All times are in Central Daylight Time unless otherwise noted.
- ^ a b c All dates are based on the local time zone where the tornado touched down; however, all times are in Coordinated Universal Time for consistency.
References[edit]
- ^ a b c d e Ostby & Pearson 1975, p. 19.
- ^ Moore & Elkins 1985, p. 41.
- ^ Hill & Turner 1977, p. 171.
- ^ Fuelberg 1979, p. 18.
- ^ a b Peslen 1979, p. 8.
- ^ Moore & Elkins 1985, p. 43.
- ^ Moore & Elkins 1985, pp. 43–44.
- ^ a b Moore & Elkins 1985, p. 44.
- ^ Moore & Elkins 1985, pp. 45.
- ^ a b c Maddox, Hoxit & Chappell 1979, p. 26.
- ^ Miller 1979, pp. 85–86.
- ^ a b c NWS Central Region 1975, p. 1.
- ^ NWS Central Region 1975, p. B1.
- ^ Weatherwise 1975, p. 184.
- ^ Peslen 1980, p. 1410.
- ^ Maddox, Hoxit & Chappell 1980, p. 329.
- ^ a b Chang, Perkey & Kreitzberg 1981, p. 1601.
- ^ NWS Central Region 1975, p. E1.
- ^ Adler & Fenn 1979, p. 516.
- ^ Dewey & Mogil 2017, p. 18.
- ^ Maddox, Hoxit & Chappell 1980, p. 327.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t u v w x y z aa ab ac ad ae af ag ah ai "Storm Data and Unusual Weather Phenomena with Late Reports and Corrections" (PDF). Storm Data. 17 (5). National Centers for Environmental Information: 2–27. May 1975. Retrieved May 17, 2024.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t Thomas P. Grazulis. Significant Tornadoes 1974–2022. pp. 22–23.
- ^ a b Wolf, Maxine (May 7, 2024). "Twister Levels Little Magnet". The Lincoln Star. Lincoln, Nebraska. p. 8 – via Newspapers.com.
- ^ "Tornadoes in 3 other towns". Columbus Telegram. No. 108. Columbus, Nebraska. United Press International. May 17, 2024. p. 1 – via Newspapers.com.
- ^ Fujita, T. Theodore (August 1981). "Tornadoes and Downbursts in the Context of Generalized Planetary Scales". Journal of the Atmospheric Sciences. 38 (8): 1511–1534. doi:10.1175/1520-0469(1981)038<1511:TADITC>2.0.CO;2.
- ^ Meyer, Joseph (May 17, 2024). "May 6, 1975 | The Omaha Tornado". KMTV 3 News Now. Omaha, Nebraska: Scripps Local Media. Retrieved May 17, 2024.
- ^ Written at Beebeetown, Iowa. "Beebeetown Farm Struck". Council Bluffs Nonpareil. No. 127. Council Bluffs, Iowa. May 7, 1975. p. 3 – via Newspapers.com.
- ^ a b "Storm Data and Unusual Weather Phenomena with Late Reports and Corrections" (PDF). Storm Data. 17 (6). National Centers for Environmental Information: 2–41. June 1975. Retrieved May 17, 2024.
- ^ NWS Storm Summary and Damage Survey - May 1975 Omaha Tornado
- ^ "Damage Photos from the '75 Omaha Tornado". NWS Omaha. NWS Omaha. Retrieved 9 October 2013.
- ^ "Omaha 5/6/75". Archived from the original on 2008-02-19. Retrieved 2008-02-27.
Sources[edit]
- Adler, Robert F.; Fenn, Douglas D. (April 1979). "Thunderstorm Intensity as Determined from Satellite Data". Journal of Applied Meteorology. 18 (4): 502–517. doi:10.1175/1520-0450(1979)018<0502:TIADFS>2.0.CO;2.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: ref duplicates default (link) - Chang, C. B.; Perkey, D. J.; Kreitzberg, C. W. (August 1981). "A Numerical Case Study of the Squall Line of 6 May 1975". Journal of the Atmospheric Sciences. 38 (8): 1601–1615. doi:10.1175/1520-0469(1981)038<1601:ANCSOT>2.0.CO;2.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: ref duplicates default (link) - Dewey, Kenneth; Mogil, H. Michael (June 23, 2017). "The Weather and Climate of Nebraska: The Heartland of Extremes". Weatherwise. 70 (4): 12–19. doi:10.1080/00431672.2017.1321919.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: ref duplicates default (link) - Fuelberg, Henry E. (August 1979). Kinetic Energy Budgets in Areas of Convection (PDF) (Contractor Report). NASA. 3166. Retrieved May 12, 2024.
{{cite tech report}}: CS1 maint: ref duplicates default (link) - Hill, Kelly; Turner, Robert E. (February 1977). "NASA's Atmospheric Variability Experiments (AVE)". Bulletin of the American Meteorological Society: 170–172. JSTOR 26218060.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: ref duplicates default (link) - Maddox, R. A.; Hoxit, L. R.; Chappell, C. F. (May 1979). Interactions Between Convective Storms and their Environment (PDF) (Contractor Report). National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Retrieved May 9, 2024.
{{cite tech report}}: CS1 maint: ref duplicates default (link)- —; Hoxit, L. Ray; Chappell, Charles F. (March 1980). "A Study of Tornadic Thunderstorm Interactions with Thermal Boundaries". Monthly Weather Review. 108 (3). American Meteorological Society: 322–336. doi:10.1175/1520-0493(1980)108<0322:ASOTTI>2.0.CO;2.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: ref duplicates default (link)
- —; Hoxit, L. Ray; Chappell, Charles F. (March 1980). "A Study of Tornadic Thunderstorm Interactions with Thermal Boundaries". Monthly Weather Review. 108 (3). American Meteorological Society: 322–336. doi:10.1175/1520-0493(1980)108<0322:ASOTTI>2.0.CO;2.
- Miller, Joseph A. (August 1979). An Example of Dry Line Convective Development: "The Omaha Tornado" (PDF) (Satellite Applications Information Note). Satellite Applications Information Notes, October 1975 – December 1978. Scott Air Force Base, Illinois: National Environmental Satellite Service. pp. 85–86. 76/12. Retrieved May 12, 2024.
{{cite tech report}}: CS1 maint: ref duplicates default (link) - Moore, James T.; Elkins, Harold A. (1985). "A Synoptic Analysis of the 6–7 May 1975 Omaha Tornado Outbreak". National Weather Digest. 10 (1). National Weather Association: 39–56. Retrieved May 9, 2024 – via CiteSeerX.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: ref duplicates default (link) - National Weather Service Central Region Headquarters (1975). The Omaha Tornado: May 6, 1975 (PDF) (Disaster Survey Report). National Weather Service. Retrieved May 9, 2024.
- Ostby, Frederick P.; Pearson, Allen (February 1976). "The Tornado Season of 1975". Weatherwise. 29 (1): 16–23. doi:10.1080/00431672.1976.10543939.
- Peslen, Cynthia A. (February 1979). Impact of Short Interval SMS Digital Data on Wind Vector Determination for a Severe Local Storms Area (PDF) (Technical Memorandum). Greenbelt, Maryland: NASA. 79714. Retrieved May 9, 2024.
- — (September 1980). "Short-Interval SMS Wind Vector Determinations for a Severe Local Storms Area". Monthly Weather Review. 108 (9): 1407–1418. doi:10.1175/1520-0493(1980)108<1407:SISWVD>2.0.CO;2.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: ref duplicates default (link)
- — (September 1980). "Short-Interval SMS Wind Vector Determinations for a Severe Local Storms Area". Monthly Weather Review. 108 (9): 1407–1418. doi:10.1175/1520-0493(1980)108<1407:SISWVD>2.0.CO;2.
- "May 1975". Weatherwise. 28 (4): 178–195. August 1975. doi:10.1080/00431672.1975.9931760.
External links[edit]
- Black Tuesday: May 6, 1975 Archived December 20, 2013, at the Wayback Machine
